Назначение этой статьи – упростить настройку DHCP сервиса для фабрики VXLAN BGP EVPN and DFA с использованием Microsoft Windows Server 2016/2019.

В официальной документации DHCP сервис на базе Microsoft Windows Server 2012 для фабрики настраивается как SuperScope, содержащий пул Loopback (в данном пуле – изюминка это исключение из пула всех IP адресов пула (excluded IP address = pool)) и пулы выдачи IP адресов для реальный сетей (здесь изюминка – настраиваются policy – в которых фильтруются DHCP Relay Circuit ID и этот DHCP relay Circuit ID содержит VNI для сети, т. е. для другого пула этот DHCP Relay Circuit ID будет чуть другим).
To configure DHCP on Windows server.
1. Create a super scope. Within the super scope, create scope B, S1, S2, S3, …, Sn for the subnet B and the subnets for each segment.
2. In scope B, specify the 'Exclusion Range' to be the entire address range (so that the offered address range must not be from this scope).
3. For every segment scope Si, specify a policy that matches on Agent Circuit ID with value of '0108000600XXXXXX', where '0108000600' is a fixed value for all segments, the 6 numbers "XXXXXX" is the segment ID value in hexadecimal. Also ensure to check the Append wildcard(*) check box.
4. Set the policy address range to the entire range of the scope.Данная статья содержит ответы на следующие вопросы:
Содержание
- ( & )
Введение
В этой части кратко перечислены все исходные данные: Инструкции по настройке сетевого оборудования, RFC используемые в DHCP пакетах в фабриках eVPN, справочно приведена эволюция настроек DHCP сервера на Microsoft Windows Server 2012 в документации Cisco. А также краткие сведения о Superscope и Policy в сервисе DHCP на серверах Microsoft Windows Server.
Как настраивается DHCP Relay на фабрике VXLAN BGP EVPN, DFA
Настройка DHCP Relay на фабрике VXLAN BGP EVPN не является основной темой этой статьи, т. к. она достаточно простая. Привожу ссылки на документацию и спойлер по настройкам на сетевом оборудовании.
Пример настройки DHCP Relay на Nexus 9000V v9.2(3)
service dhcp
ip dhcp relay
ip dhcp relay information option
ip dhcp relay information option vpn
interface loopback10
vrf member VRF1
ip address 10.120.0.1/32 tag 1234567
interface Vlan12
no shutdown
vrf member VRF1
no ip redirects
ip address 10.120.251.1/24 tag 1234567
no ipv6 redirects
fabric forwarding mode anycast-gateway
ip dhcp relay address 10.0.0.5
ip dhcp relay source-interface loopback10
RFC которые реализованы в работе сервиса DHCP Relay в фабриках VXLAN BGP EVPN
RFC#6607: Sub-option 151(0x97) — Virtual Subnet Selection
• Sub-option 151(0x97) - Virtual Subnet Selection (Defined in RFC#6607)
Used to convey VRF related information to the DHCP server in an MPLS-VPN and VXLAN EVPN multi-tenant environment.Передается «имя» VRF в котором находиться клиент.
RFC#5107: Sub-option 11(0xb) — Server ID Override
• Sub-option 11(0xb) - Server ID Override (Defined in RFC#5107.)
The server identifier (server ID) override sub-option allows the DHCP relay agent to specify a new value for the server ID option, which is inserted by the DHCP server in the reply packet. This sub-option allows the DHCP relay agent to act as the actual DHCP server such that the renew requests will come to the relay agent rather than the DHCP server directly. The server ID override sub-option contains the incoming interface IP address, which is the IP address on the relay agent that is accessible from the client. Using this information, the DHCP client sends all renew and release request packets to the relay agent. The relay agent adds all of the appropriate sub-options and then forwards the renew and release request packets to the original DHCP server. For this function, Cisco’s proprietary implementation is sub-option 152(0x98). You can use the ip dhcp relay sub-option type cisco command to manage the function.Опция используется для того, чтобы клиент посылал запрос о перепродлении аренды адреса на IP адрес используемый в этой опции. (В Cisco VXLAN BGP EVPN – это Anycast адрес шлюза по умолчанию для клиента.)
RFC#3527: Sub-option 5(0x5) — Link Selection
Sub-option 5(0x5) - Link Selection (Defined in RFC#3527.)
The link selection sub-option provides a mechanism to separate the subnet/link on which the DHCP client resides from the gateway address (giaddr), which can be used to communicate with the relay agent by the DHCP server. The relay agent will set the sub-option to the correct subscriber subnet and the DHCP server will use that value to assign an IP address rather than the giaddr value. The relay agent will set the giaddr to its own IP address so that DHCP messages are able to be forwarded over the network. For this function, Cisco’s proprietary implementation is sub-option 150(0x96). You can use the ip dhcp relay sub-option type ciscocommand to manage the function.Адрес сети, из которой клиенту необходим IP адрес.
Эволюция документации Cisco в части настройки DHCP на Microsoft Windows Server 2012
Включил этот раздел потому, что прослеживается положительная тенденция со стороны вендора:
В документации приведена только настройка DHCP Relay на сетевом оборудовании.
Для настройки DHCP на Windows Server 2012 использовалась другая статья:
В этой статье указывается, что для каждой сети/VNI необходима своя связка SuperScope и свой собственный набор Loopback адресов:
If multiple DHCP Scopes are required for multiple subnets, you need to create one LoopbackX per subnet/vlan on all LEAFS and create a superscope with a loopbackX range scope and actual client IP subnet scope per vlan.
Добавили настройки Windows 2012 Server в документацию по настройке сетевого оборудования. Для всех используемых пулов адресов необходим один SuperScope на ЦОД и этот SuperScope является границей ЦОД:
Create Superscope for all scopes you want to use for Option 82-based policies.
Note
The Superscope should combine all scopes and act as the administrative boundary.
Очень емко рассказано обо всем:
Let us assume the switch is using the address from subnet B (it can be the backbone subnet, management subnet, or any customer designated subnet for this purpose) to communicate with the Windows DHCP server. In DFA we have subnets S1, S2, S3, …, Sn for segment s1, s2, s3, …, sn.
To configure DHCP on Windows server.
1. Create a super scope. Within the super scope, create scope B, S1, S2, S3, …, Sn for the subnet B and the subnets for each segment.
2. In scope B, specify the 'Exclusion Range' to be the entire address range (so that the offered address range must not be from this scope).
3. For every segment scope Si, specify a policy that matches on Agent Circuit ID with value of '0108000600XXXXXX', where '0108000600' is a fixed value for all segments, the 6 numbers "XXXXXX" is the segment ID value in hexadecimal. Also ensure to check the Append wildcard(*) check box.
4. Set the policy address range to the entire range of the scope.
DHCP в Microsoft Windows Server (superscope & policy)
Superscope is an administrative feature of a DHCP server that can be used to group multiple scopes as a single administrative entity. Superscope allows a DHCP server to provide leases from more than one scope to clients on a single physical network. Scopes added to a superscope are called member scopes. Что такое SuperScope – это функционал, позволяющий объединить несколько пулов IP адресов в одну административную единицу. Чтобы анонсировать пользователям в одной физической сети (в одном VLAN) ip адреса из нескольких пулов. Если запрос пришел к пулу адресов в составе SuperScope, то выдать клиенту адрес можно из другого Scope входящего в этот SuperScope.
The DHCP Server role in Windows Server 2012 introduces a new feature that allows you to create IPv4 policies that specify custom IP address and option assignments for DHCP clients based on a set of conditions.
The policy based assignment (PBA) feature allows you to group DHCP clients by specific attributes based on fields contained in the DHCP client request packet. PBA enables targeted administration and greater control of the configuration parameters delivered to network devices with DHCP. Политики – позволяют назначать пользователям IP адреса в зависимости от типа пользователя или параметра. Инженеры Cisco используют политики в Windows Server 2012 для фильтрации по VNI (Virtual Network Identifier).
Основная часть
В данном разделены проведены результаты исследований, почему не поддерживается, как это работает (логика), что нового и как это новое нам поможет.
Почему не поддерживается Microsoft Windows Server 2000/2003/2008?
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 и более ранние версии не обрабатывают опцию 82 (Option 82) и обратный пакет отправляют без опции 82.
- Запрос от клиента отправляется Broadcast (DHCP Discover).
- Оборудование (Nexus) отправляет пакет к DHCP серверу (DHCP Discover + Option 82).
- DHCP Сервер принимает пакет обрабатывает, отправляет обратно, но без опции 82. (DHCP Offer – without option 82)
- Оборудование (Nexus) принимает пакет от DHCP сервера. (DHCP Offer) Но не отправляет этот пакет к конечному пользователю.
Данные снифера — на Windows Server 2008 и на клиенте DHCPWindows Server 2008 получает запрос от сетевого оборудования. (Option 82 присутствует в списке)
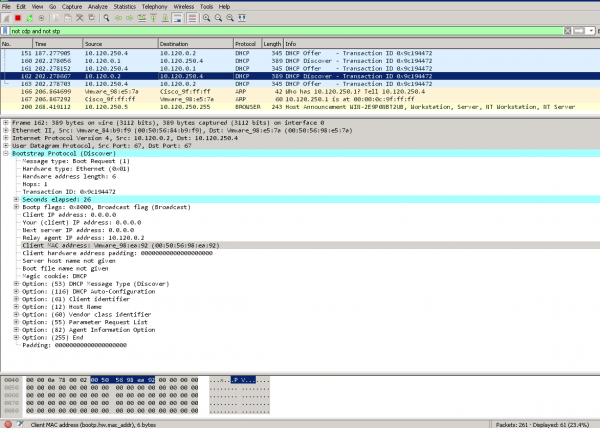
Windows Server 2008 отправляет ответ к сетевому оборудованию. (Option 82 отсутствует в списке опций в пакете)
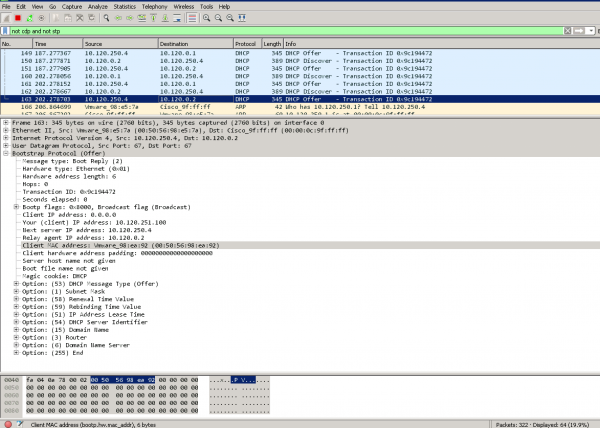
Запрос от клиента – присутствуют DHCP Discover и отсутствуют DHCP Offer
Статистика на сетевом оборудовании:
NEXUS-9000V-SW-1# show ip dhcp relay statistics
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Message Type Rx Tx Drops
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Discover 8 8 0
Offer 8 8 0
Request(*) 0 0 0
Ack 0 0 0
Release(*) 0 0 0
Decline 0 0 0
Inform(*) 0 0 0
Nack 0 0 0
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Total 16 16 0
----------------------------------------------------------------------
DHCP L3 FWD:
Total Packets Received : 0
Total Packets Forwarded : 0
Total Packets Dropped : 0
Non DHCP:
Total Packets Received : 0
Total Packets Forwarded : 0
Total Packets Dropped : 0
DROP:
DHCP Relay not enabled : 0
Invalid DHCP message type : 0
Interface error : 0
Tx failure towards server : 0
Tx failure towards client : 0
Unknown output interface : 0
Unknown vrf or interface for server : 0
Max hops exceeded : 0
Option 82 validation failed : 0
Packet Malformed : 0
Relay Trusted port not configured : 0
DHCP Request dropped on MCT : 0
* - These counters will show correct value when switch
receives DHCP request packet with destination ip as broadcast
address. If request is unicast it will be HW switched
NEXUS-9000V-SW-1#
Почему в Microsoft Windows Server 2012 настройка такая сложная?
В Microsoft Windows Server 2012 еще не поддерживается RFC#3527 (Option 82 Sub-option 5(0x5) — Link Selection)
Но уже реализован функционал Policy.
Как это работает:
- Microsoft Windows Server 2012 есть супер-пул (SuperScope) в котором есть адреса Loopback и пулы для реальных сетей.
- Выбор пула для выдачи IP адреса попадает в SuperScope, т. к. ответ пришел от DHCP Relay с Source адреса Loopback, входящего в SuperScope.
- Используя Policy запрос выбирает из Superscope тот member scope, VNI которого содержится в Option 82 Suboption 1 Agent Circuit ID. (“0108000600”+ 24 бита VNI + 24 бита значения которых мне неизвестно, но сниффер показывает значения 0 в этом поле.)
Как упрощается настройка в Microsoft Windows Server 2016/2019?
В Microsoft Windows Server 2016 реализован функционал RFC#3527. Т. е. Windows Server 2016 умеет распознавать правильную сеть из атрибута Option 82 Sub-option 5(0x5) — Link Selection
Возникают сразу 3 вопроса:
- Можем ли обойтись без Superscope?
- Можем ли обойтись без Policy и перевода VNI в 16-тиричный вид?
- Можем ли обойтись без Scope для Loopback адресов DHCP Source?
Q. Можем ли обойтись без Superscope?
A. Да, scope можно создавать сразу в области IPv4 адресов.
Q. Можем ли обойтись без Policy и перевода VNI в 16-тиричный вид?
A. Да, выбор сети происходит на основе Option 82 Suboption 0x5,
Q. Можем ли обойтись без Scope для Loopback адресов DHCP Source?
A. Нет, не можем. Т. к. в Microsoft Windows Server 2016/2019 действует защита от злонамеренных DHCP запросов. Т. е. все запросы с адресов, которых нет в пуле DHCP сервера считаются злонамеренными.
Note
All relay agent IP addresses (GIADDR) must be part of an active DHCP scope IP address range. Any GIADDR outside of the DHCP scope IP address ranges is considered a rogue relay and Windows DHCP Server will not acknowledge DHCP client requests from those relay agents.
A special scope can be created to "authorize" relay agents. Create a scope with the GIADDR (or multiple if the GIADDR's are sequential IP addresses), exclude the GIADDR address(es) from distribution, and then activate the scope. This will authorize the relay agents while preventing the GIADDR addresses from being assigned.Т.е. для настройки на Microsoft Windows Server 2016/2019 DHCP пула для VXLAN BGP EVPN фабрики необходимо только:
- Создать пул для Source адресов Relay.
- Создать пул для клиентских сетей
Что не является необходимым (но можно настроить и это будет работать, и не будет мешать работать):
- Создавать Policy
- Создавать SuperScope
ПримерПример настройки DHCP сервера (присутствуют 2 реальных клиента DHCP — клиенты подключены к VXLAN фабрике)
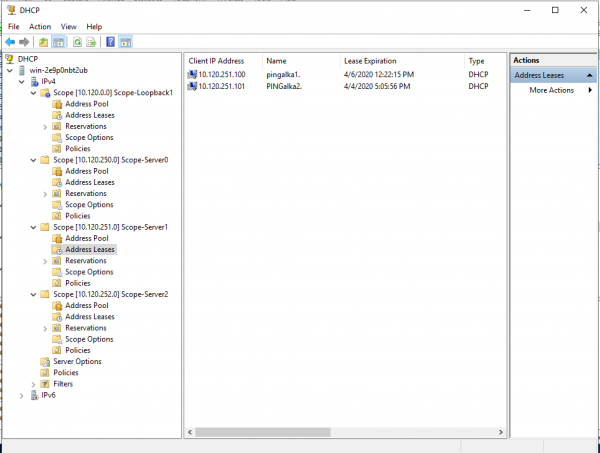
Пример настройки пользовательского пула:
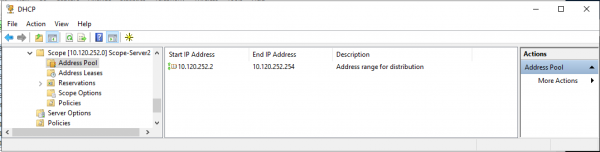
Пример настройки пользовательского пула (выбраны политики — для доказательства что политики не использовались для корректной работы пула):
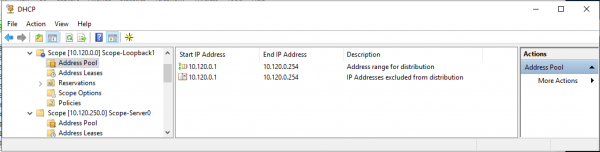
Пример настройки пула для Source адресов DHCP Relay (диапазон адресов для выдачи полностью соответствует исключению из пула адресов):
Настройка DHCP сервиса на Microsoft Windows Server 2019
Настройка пула для Loopback адресов (source) для DHCP Relay.
Создаем новый пул (Scope) в пространстве IPv4.
Мастер создания пула. «Next >»
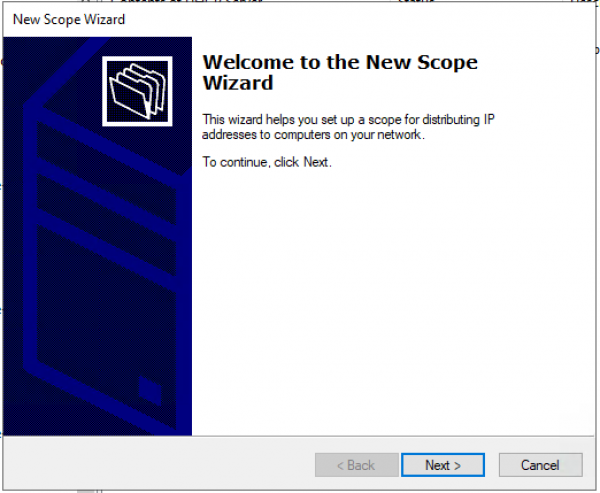
Настраиваем имя пула и описание (Description) пула.
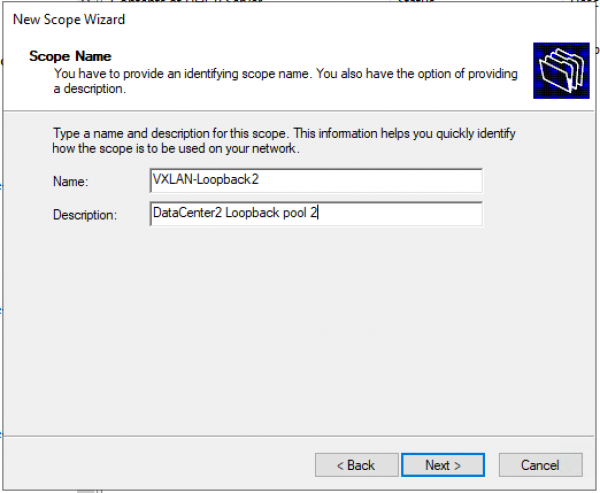
Задаем диапазон IP адресов для Loopback и маску для пула.
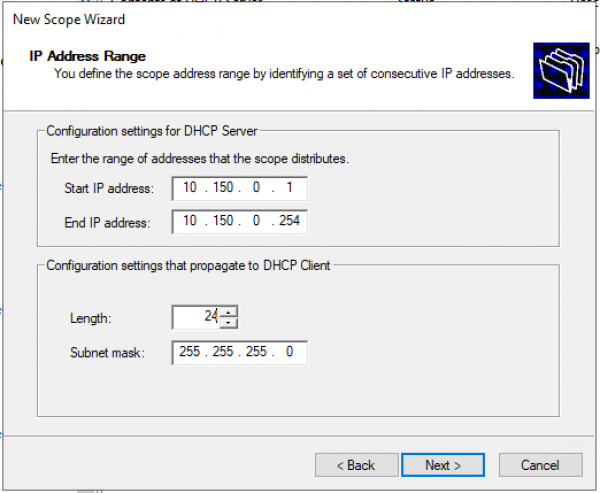
Добавляем исключения. Диапазон исключений должен полностью совпадать с диапазоном пула.
Время аренды. «Next >»
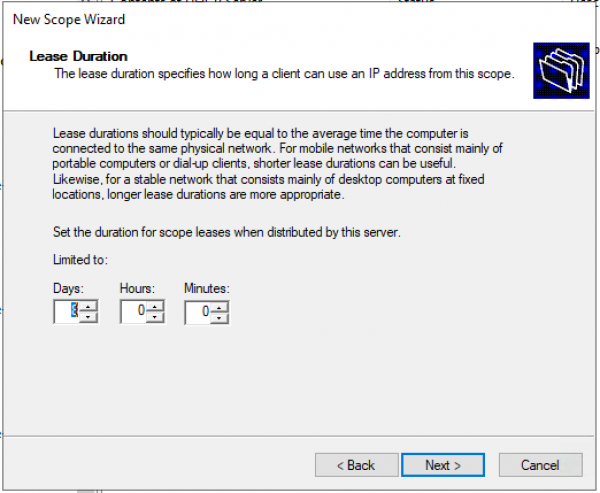
Запрос: Будете настраивать DHCP опции сейчас (DNS, WINS, Gateway, Domain) или сделаете это позже. Быстрее будет ответить нет, и после активировать пул вручную. Либо пройти до конца не заполняя ни какую информацию и в конце мастера активировать пул.
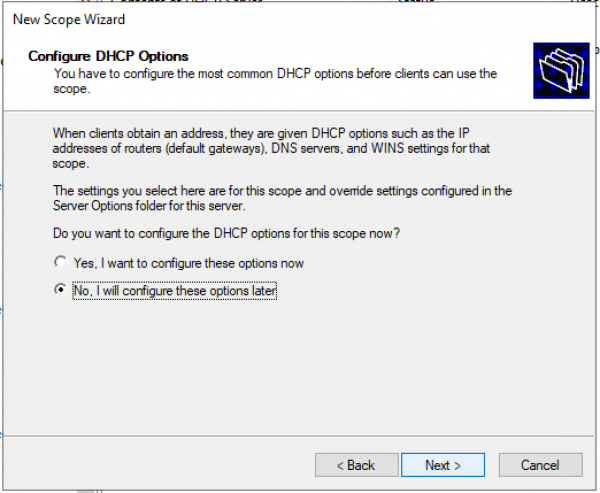
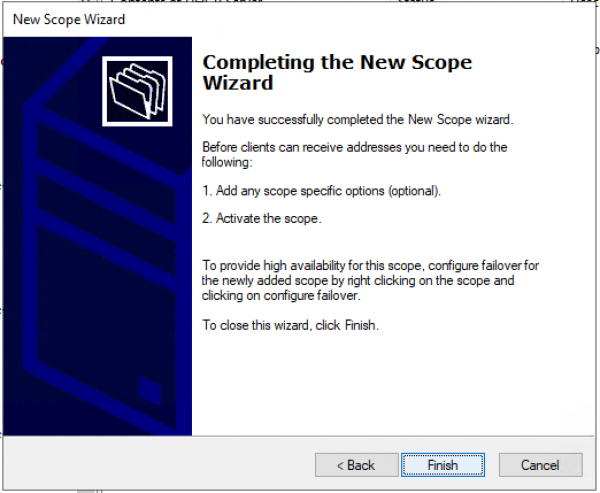
Подтверждаем, что опции не настроены, пул не активирован. «Finish»
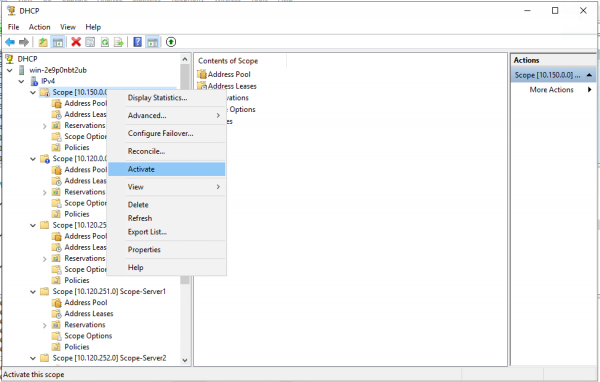
Активируем пул вручную. — Выбираем Scope и в контекстном меню — выбираем «Activate».
Создаем пул для пользователей/серверов.
Создаем новый пул.
Мастер создания пула. «Next >»
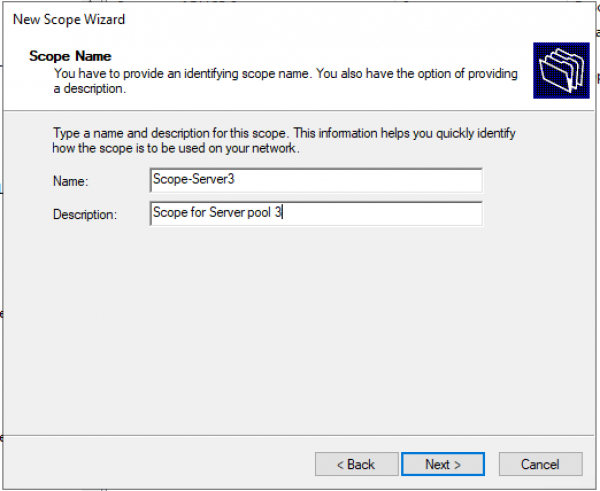
Настраиваем имя пула и описание (Description) пула.
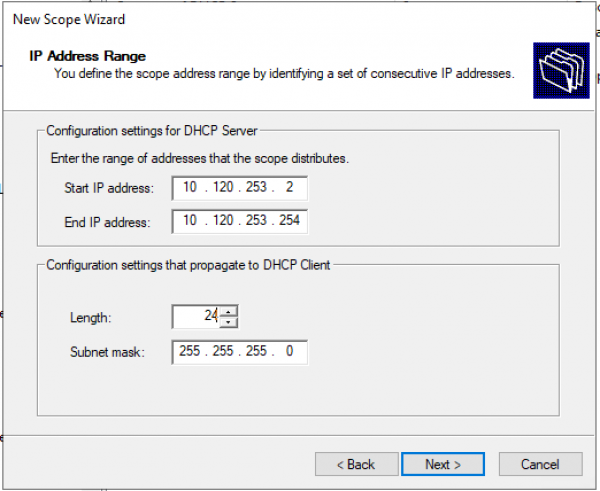
Задаем диапазон IP адресов для Loopback и маску для пула.
Добавляем исключения. (По умолчанию исключений не требуется) «Next >»
Время аренды. «Next >»
Запрос: Будете настраивать DHCP опции сейчас (DNS, WINS, Gateway, Domain) или сделаете это позже. Да настроим сейчас.
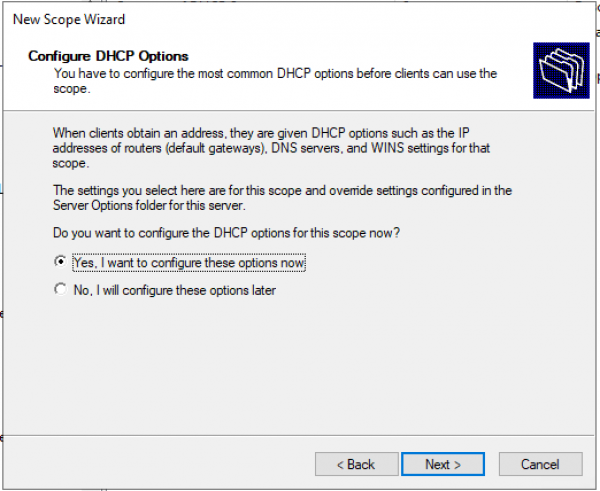
Настраиваем адрес шлюза по умолчанию.
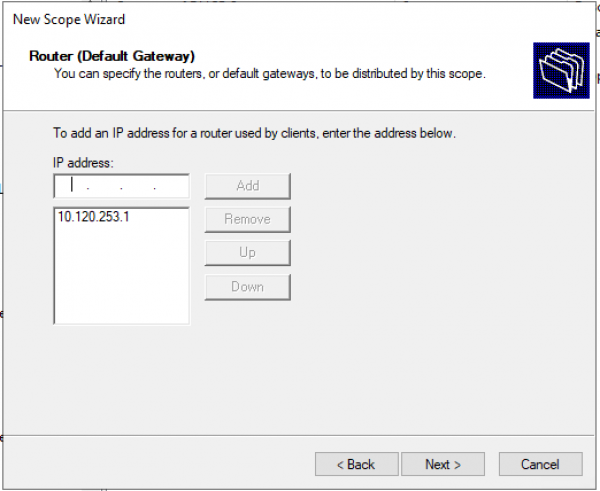
Настраиваем домен и адреса DNS серверов.
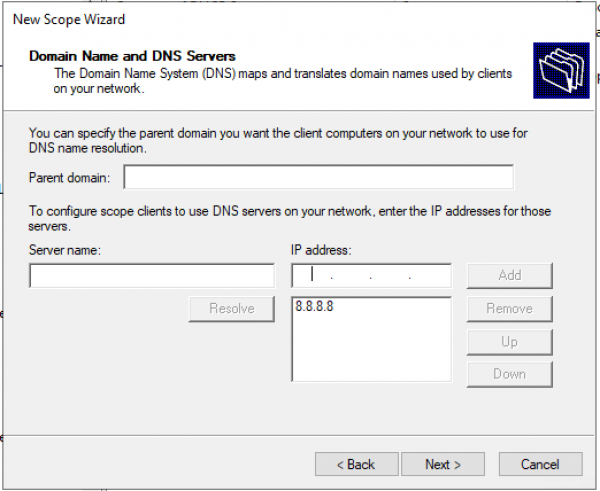
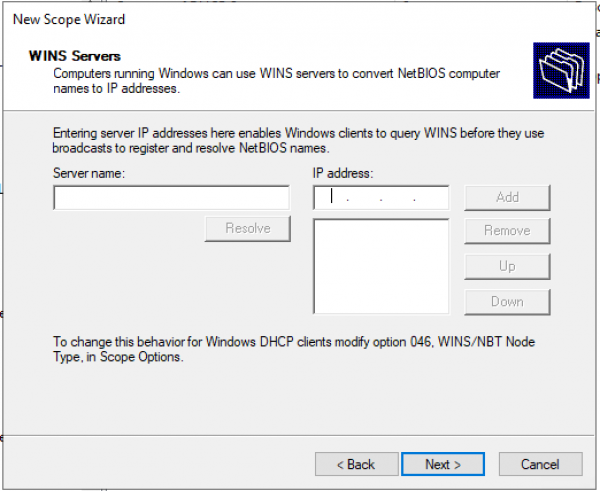
Настраиваем IP адреса WINS серверов.
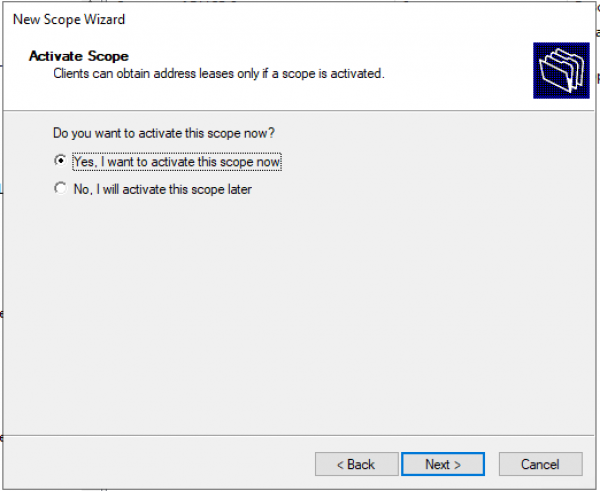
Активация Scope.
Пул настроен. «Finish»
Заключение
Использование Windows Server 2016/2019 уменьшает сложность настройки DHCP сервера для VXLAN фабрики (или любой другой фабрики). (Не требуется передача IT специалистам специальные связки: Network/Agent Circuit ID для прописывания фильтров.)
Будет ли работать конфигурация для Windows Server 2012 на новых серверах 2016/2019 – да будет работать.
В данном документе приведены ссылки на 2 версии: 7.X и 9.3. Это связано с тем, что версия 7.0(3)I7(7) — Cisco Suggested release, а версия 9.3 — является самой инновационной (вплоть до поддержки Multicast через VXLAN Multisite).
Список источников
Источник: habr.com



